What is Coronary Artery Disease?
Coronary artery disease (CAD) is the narrowing or blockage of the coronary arteries caused by atherosclerosis.
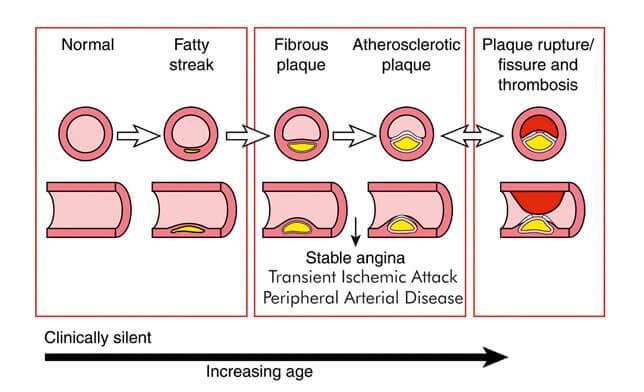
- Atherosclerosis (sometimes called “hardening” or “clogging” of the arteries) is the build-up of cholesterol, and fatty deposits (called plaque) on the inner walls of the arteries that restrict blood flow to the heart
- Without adequate blood, the heart becomes starved of oxygen and the vital nutrients it needs to work properly. This can cause chest pain called angina.
- When one or more of the coronary arteries are completely blocked, a heart attack (injury to the heart muscle) may occur.
Progression of Atherosclerosis
Risk Factors of CAD
Risk factors are traits and lifestyle habits that increase your chance of disease. The more risk factors you have, the higher your changes of having a heart attack or stroke.
Uncontrollable Risk factors
Coronary artery disease (CAD) is the narrowing or blockage of the coronary arteries caused by atherosclerosis.
- Increasing age: The older you get the more likely you are to develop heart disease or have a heart attack or stroke.
- Gender: Males have a greater risk of heart attacks and have heart attacks earlier than women do.
- Previous heart attack or stroke: If you’ve had a heart attack or stroke you’re at a higher risk of having a second heart attack or stroke.
- Family history of heart attack or stroke: The chance of a stroke is greater in people who have a family history of stroke.
Controllable Risk Factors
CERTAIN RISK FACTORS CAN BE MODIFIED OR CHANGED, THESE INCLUDE:
- High blood pressure
- High blood cholesterol
- Cigarette smoking or exposure to second hand smoke
- Lack of physical activity
- Obesity
- Diabetes
Your Treatment Options
- Treatment of coronary artery disease is aimed at controlling symptoms and allowing or stopping the progression of disease
- The method of treatment is based on many factors determined by your symptoms, a physical exam and diagnostic testing. You may be asked to change the lifestyle, physical activity and diet control.
- If the blockage is less than 70 percent, medications may be the first line of treatment and If greater than that you might be asked for angioplasty with or without stent or coronary artery bypass surgery (CABG)
- To prevent damage to your heart muscle, do not delay seeking medical treatment
A. Balloon Angioplasty
- The angioplasty procedures may sometimes be performed without stent deployment, a technique that is now referred as plain old balloon angioplasty (POBA)
- A balloon catheter is a type of soft catheter with an inflatable balloon at its tip which was used during a catheterization procedure to enlarge a narrow opening or passage within the body.
- The deflated balloon catheter is positioned, then inflated to perform the necessary procedure, and deflated again in order to be removed.
B. Angioplasty and Stenting
- The angioplasty procedures may sometimes be performed without stent deployment, a technique that is now referred as plain old balloon angioplasty (POBA)
- A balloon catheter is a type of soft catheter with an inflatable balloon at its tip which was used during a catheterization procedure to enlarge a narrow opening or passage within the body.
- The deflated balloon catheter is positioned, then inflated to perform the necessary procedure, and deflated again in order to be removed.
C. What is a stent?
Coronary artery stents
A stent is a small, metal mesh tube that acts as a scaffolding to provide support inside the coronary artery. The shape and material of the stent results in a flexibility which can be expanded by a balloon to adapt to the shape and curves of the artery.
Stent implantation
Stent is introduced into the blood vessel through the femoral or radial artery on a balloon catheter and advanced to the blocked area of the artery. The balloon in then inflated, which causes the stent to expand until it fits the inner wall of the artery. The balloon is deflated and withdrawn. Stent stays in place permanently, holding the vessel open and improving the flow of blood.
Restenosis
Re-narrowing of coronary artery after it has been treated with either balloon or with the stent. The re-narrowing can be caused by vessel recoil and formation of tissue growth in the treated area. The rate of restenosis in the patient treated with balloon is upto 30 to 50% and with the stent (without drug) is upto 10 to 30%
Fully Bioresorbable scaffolds
The Bioresorbable vascular Scaffold(BRS) are the latest development in interventional cardiology. BRS provides a temporary scaffold to the lesion. Once the vessel blockage is treated and healing is completed, BRS degrades completely , leaving the artery in its natural state with no foreign residue. This provides both physicians and patients the room to explore future treatment interventions, if required, in the same blood vessel.
